What is Compound Interest and Why is it Important?

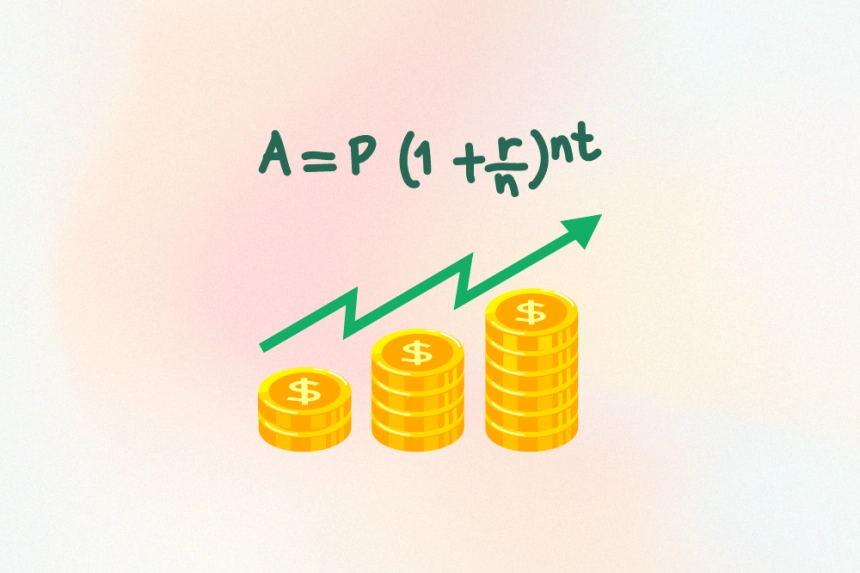
Compound interest is one of the most fundamental concepts in the world of finance and investment. Understanding how it works can have a significant impact on the financial health of an individual or a business. In this article, we will explore in depth what compound interest is, how it is calculated, and why it is crucial for achieving certain financial goals.
What is Compound Interest?
Compound interest is the process by which interest generated from an investment or loan is added to the principal amount, forming a new principal on which future interest is calculated. In other words, interest is calculated not only on the original capital but also on the already accumulated interest.
Difference Between Simple Interest and Compound Interest
To better understand compound interest, it is helpful to compare it to simple interest. Simple interest is calculated only on the original amount of money, without taking into account the accumulated interest. Below is a summary of the key differences:
Characteristic Simple Interest Compound Interest
| Calculation | Only on the initial principal | On the principal plus accumulated interest
| Increase | Linear | Exponential
| Usage | Less common in investments | Common in finance and investments
This difference translates into compound interest tending to generate more wealth over time.
How is Compound Interest Calculated?
Calculating compound interest may seem complicated, but the formula is quite simple. The basic formula for calculating the total amount ( A ) after ( n ) years is as follows:
[ A = P (1 + r/n)^{nt} ]
where:
- ( A ) = Total amount after ( t ) years
- ( P ) = Initial principal (capital)
- ( r ) = Annual interest rate (decimal)
- ( n ) = Number of times interest is compounded per year
- ( t ) = Number of years
Example Calculation
Suppose you invest $1,000 at an annual interest rate of 5% compounded annually for 10 years. Using the formula, the calculation would be as follows:
- ( P = 1000 )
- ( r = 0.05 )
- ( n = 1 ) (annual compounding)
- ( t = 10 )
Substituting into the formula:
[ A = 1000 (1 + 0.05/1)^{1 \cdot 10} ] [ A = 1000 (1 + 0.05)^{10} ] [ A = 1000 (1.62889) ] [ A \approx 1628.89 ]
Thus, after 10 years, you would have approximately $1,628.89.
Why is Compound Interest Important?
Compound interest has several important implications in personal finance and investment. Here are some key reasons why it is essential to understand and apply this concept.
Exponential Growth of Investment
One of the most powerful characteristics of compound interest is its ability to produce exponential growth of investments. The longer money is left invested, the greater the effect of compound interest. This means that investing early can lead to substantial long-term returns.
Saving for the Future
While compound interest can benefit investors, it is also crucial for savers. If you have a savings account that pays compound interest, your money will grow faster than in an account that offers simple interest. This is particularly important for saving for retirement, education, or any other long-term goal.
Debt
On the other hand, compound interest can also affect those with debt. In the case of loans, compound interest can significantly increase the total amount that must be repaid. Understanding how it works can help borrowers better manage their debts and avoid overindebtedness.
Strategies to Take Advantage of Compound Interest
To maximize the benefits of compound interest, consider the following strategies:
Start Saving and Investing Early
The general rule is that the longer you leave your money invested, the greater the benefit from compound interest. Starting to save at a young age can make a significant difference.
Increase Your Contributions
Increasing the amounts you contribute to your investments or savings can have a significant effect on their growth. This is especially important in retirement accounts and investment funds.
Reinvest Interest
If you receive interest from your investments, reinvest that money instead of withdrawing it. This allows your capital to grow more quickly due to compound interest.
Conclusion
Compound interest is a critical concept in finance that can influence your economic future. Understanding it and applying it correctly can allow you to build wealth, save more effectively, and manage your debts better. The key is to start as early as possible and harness the power of compound interest to your advantage.
If you want to learn more about personal finance or investment, we encourage you to explore other resources or consult with a financial advisor. Your financial future may depend on it!








